Optical Isolator: A Complete Guide to Working Principle, Types & Applications (2025)
An optical isolator is a passive component that allows light to travel in only one direction, blocking reflected or backward-propagating light. It plays a critical role in protecting sensitive optical sources—such as lasers—from feedback that could cause instability, noise, or damage. Similar to a diode in electronic circuits, an optical isolator ensures unidirectional transmission.
Types of Optical Isolators: Polarization-Dependent vs Independent
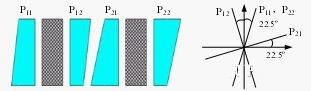
Polarization-Dependent (Free-Space) Isolator
Used primarily with semiconductor lasers, where the input light has stable polarization. Compact and cost-effective, it’s commonly found in laser modules.Polarization-Independent (In-Line) Isolator
Designed for fiber communication systems and EDFAs, where polarization states are unpredictable. It maintains performance regardless of input polarization, making it ideal for telecom and long-haul networks.
Working Principle
The operation relies on two key principles:
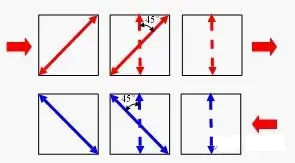
Faraday magneto-optical effect: A Faraday rotator rotates the polarization of light by 45° under a magnetic field.
Malus’ law: Only light aligned with a polarizer’s axis can pass through.
In the forward direction, incoming light passes through the first polarizer, is rotated by 45° in the Faraday rotator, and aligns perfectly with the second polarizer—allowing full transmission.
In the reverse direction, reflected light passing back through the rotator is rotated another 45° in the same direction (non-reciprocal), resulting in a 90° misalignment with the first polarizer—blocking the light completely.
Pic 1: optical isolator working principle diagram
In-Line Optical Isolator Designs: Wedge, Displacer & Dual-Stage
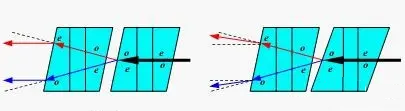
Displacer-Type
Uses birefringent crystals to separate and recombine light beams. However, it requires large crystals for sufficient isolation, leading to bulky and expensive devices—now largely outdated.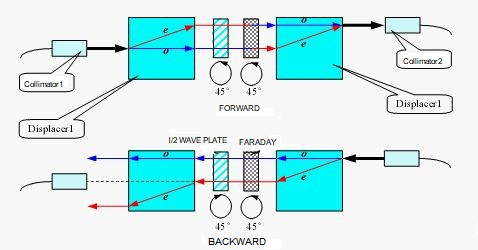
Pic 2: displacer-type optical isolator designWedge-Type
The most widely used design today. It uses wedge-shaped birefringent crystals to angularly deflect reverse light, preventing it from coupling back into the input fiber. It’s compact, cost-effective, and offers high isolation.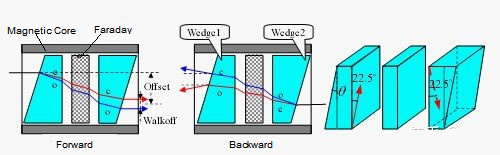
Pic 3: wedge-type optical isolator design
Dual-Stage Isolator
Combines two isolator stages in series to achieve higher isolation (>50 dB) over a broader wavelength range. It compensates for limitations like Faraday rotator extinction ratio and wavelength sensitivity, making it suitable for high-performance applications.
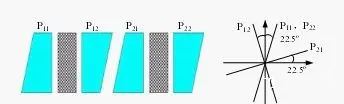
Pic 4: dual stage optical isolator for high isolation
Performance Considerations
PMD (Polarization Mode Dispersion): Introduced due to birefringence; can be compensated with additional crystal elements.
PDL (Polarization Dependent Loss): Kept low through precise design.
Assembly Precision: Critical for dual-stage isolators to maintain high isolation and yield.
Pic 5: polarization independent in-line isolator
Ideal for use in:
Laser systems, fiber amplifiers (EDFA), high-speed optical transceivers, and dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) networks.
This concise version keeps your technical credibility while being accessible to engineers, buyers, and international clients.
Looking for a reliable optical isolator supplier?
Guilin GLSUN offers high-performance in-line and free-space isolators for telecom, laser, and EDFA applications.





 Guanglong S&T Zone, No.8 High-tech Industry Park Chaoyang Road, Guilin ,Guangxi, China
Guanglong S&T Zone, No.8 High-tech Industry Park Chaoyang Road, Guilin ,Guangxi, China  +86-133-4600-8527
+86-133-4600-8527  alan.shizz@glsun.com
alan.shizz@glsun.com