Introduction of PON
What is PON?
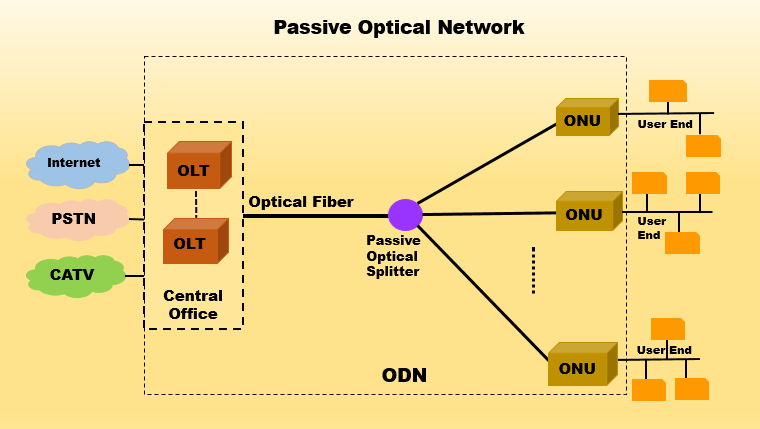
PON is a passive optical network, which means there is not any active equipment but only optical fiber and passive components in the ODN (Optical Distribution Network) between OLT (Optical Line Terminal) and ONU (Optical Network Unit). PON mainly adopts point-to-multi-point network structure, which is the main technology to achieve FTTB/FTTH.
Three basic functional modules
OLT: Optical Line Terminal is simply the "upstream" operator-side equipment end of optical fiber network transmission. OLT is the core device in the PON network and is usually located at the central office of the operator. It is responsible for connecting with the core network while providing optical signals to the ONU. The OLT has multiple PON ports and can support multiple users to access at the same time. The main functions of the OLT include signal modulation, demodulation, multiplexing and transmission, etc., which can convert the signal from the core network into optical signals and transmit them to the ONU through the ODN network.

ONU: ONU is a user-side device in a PON network that is usually placed on the user side. It is responsible for converting the received optical signal into an electrical signal and transmitting it to the user's device (such as a computer, telephone, or television). The ONU has multiple Ethernet ports and can support multiple user devices to access at the same time. The main functions of the ONU include signal demodulation, multiplexing and transmission, etc., which can convert the optical signal from the OLT into an electrical signal and transmit it to the user device through the Ethernet port.
ODN: ODN is the optical cable part of the PON network, which connects OLT and ONU/ONT and is responsible for transmitting optical signals. ODN is usually composed of optical fibers, optical cables,optical connector (pigtail) and optical splitters, etc., which can be flexibly expanded and configured. ODN plays a vital role in the PON network, and its performance directly affects the performance and stability of the entire network. Therefore, operators need to plan and optimize ODN in detail when designing and deploying PON networks.
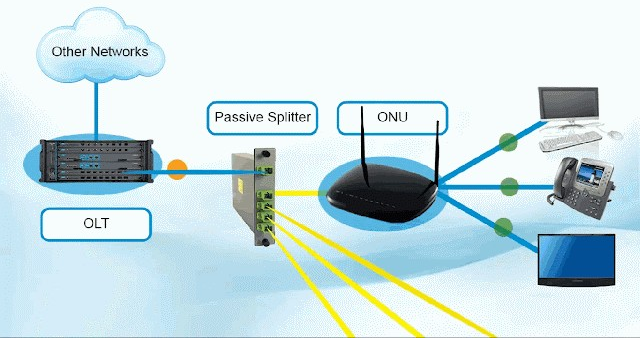
Commons type of PON
PON has developed and evolved various technical solutions in different time periods, including:
APON:passive optical network based on ATM technology
BPON: broadband passive optical network(new name of APON)
EPON:Ethernet passive optical network
GPON:Gigabit passive optical network
XG-PON/XGS-PON:10G-Gigabit passive optical network
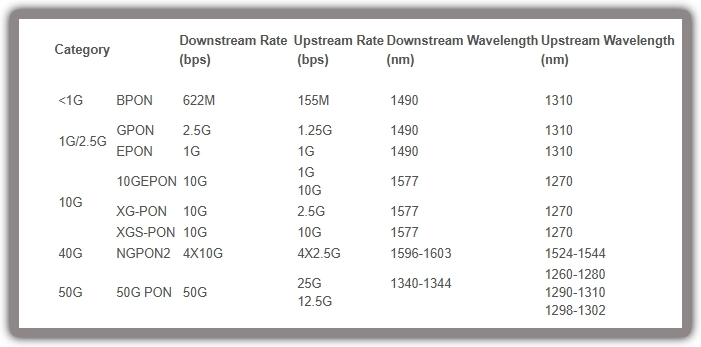
EPON, GPON, 10G-EPON and XG-PON, the main differences are in line speed, available bandwidth and working wavelength.
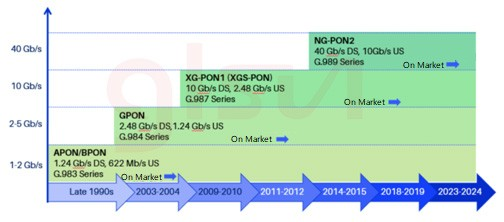
Development history of PON
GPON: GPON → XGPON/XGS PON → NG-PON2
EPON: EPON → 10G EPON → NG-EPON
Advantages of PON
1. High Bandwidth: EPON/GPON is upgraded to 1G/2.5G-10G-25G/50G with the development of Ethernet technology.
2. Strong anti-interference capability: PON is a pure medium network that completely avoids electromagnetic interference and lightning impacts from external devices, making it highly suitable for use in areas with harsh natural conditions
3. Low cost: PON equipment is simple, small in size, and has low installation and maintenance costs, resulting in reduced investment. This can significantly lower construction costs and accelerate the popularization and promotion of networks.





 Guanglong S&T Zone, No.8 High-tech Industry Park Chaoyang Road, Guilin ,Guangxi, China
Guanglong S&T Zone, No.8 High-tech Industry Park Chaoyang Road, Guilin ,Guangxi, China  +86-133-4600-8527
+86-133-4600-8527  alan.shizz@glsun.com
alan.shizz@glsun.com