What is C band and L band in WDM
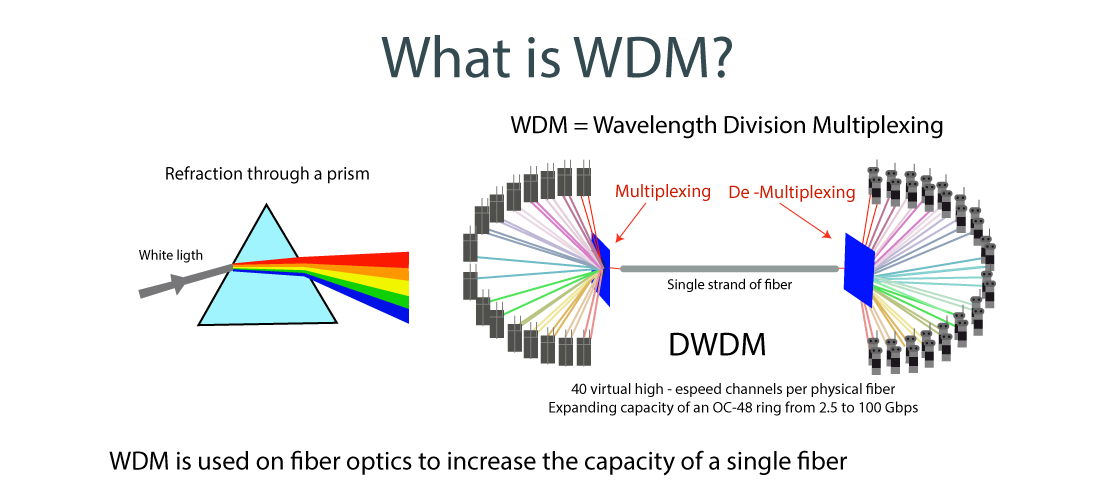
What is WDM?
WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing ) is a transmission technology that uses one optical fiber to simultaneously transmit multiple optical carriers of different wavelengths. The transmission loss in optical fiber varies with the wavelength of light. In order to reduce loss as much as possible and ensure transmission effect, it is necessary to find the most suitable wavelength for transmission. After a long time of exploration and testing, light in the wavelength range of 1260nm~1625nm has the lowest signal distortion and loss caused by dispersion, and is most suitable for transmission in optical fiber.
The wavelength applications of optical fibers are divided into several bands, and each band is used as an independent channel to transmit an optical signal of a predetermined wavelength. ITU-T divides the frequency band of single-mode optical fiber more than 1260nm into several bands: O, E, S, C, L and U.
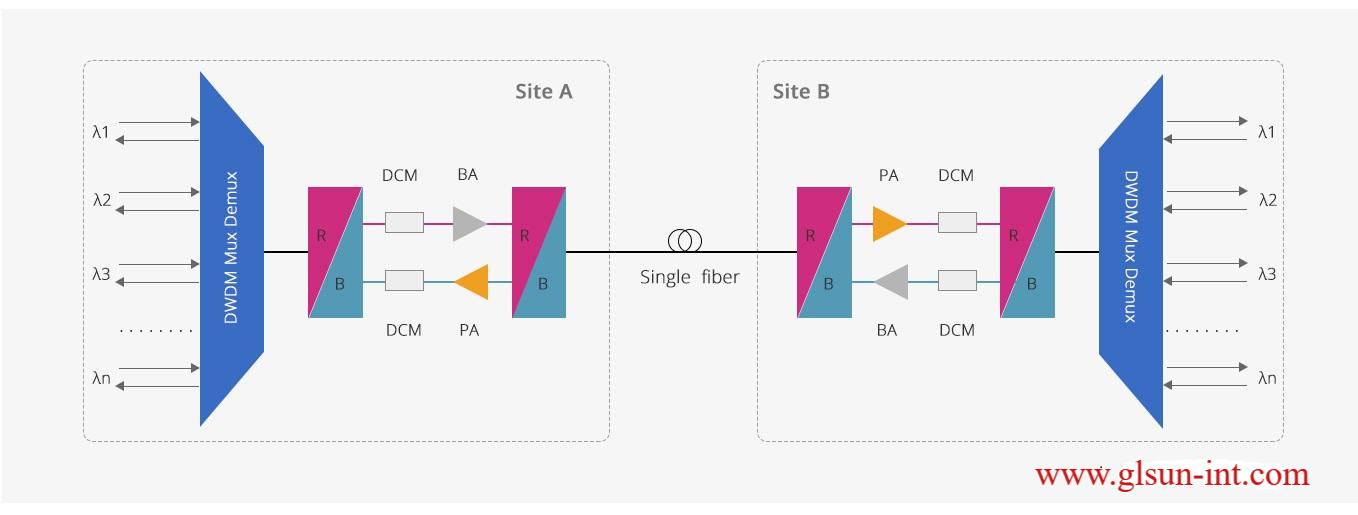
O Band
O band is the original band with wavelength range 1260-1360 nm. O band is the first wavelength band historically used for optical communication, with minimal signal distortion (due to dispersion).
E Band
E band is the extended band with wavelength range 1360-1460 nm. It is the least common of these wavebands. E band is mainly used as an extension of O band, but its use in optical communications is limited mainly because many existing optical cables show high attenuation in E band and the manufacturing process is very energy intensive.
S Band
E band is the short wavelength band with wavelength range 1460-1530 nm. Fiber loss is lower in S band than in O band, and S band is used by many PON (passive optical network) systems.
C Band
C band is the conventional wavelength band with wavelength range 1530-1565 nm. Optical fiber has the lowest loss in C band and has a great advantage in long distance transmission system. EDFA technology is commonly used in many metropolitan, long-distance, ultra-long-distance and subsea optical transmission systems in combination with WDM. The use of C band has expanded with the advent of DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing), which enables multiple signals to share a single optical fiber.
L Band
C band is the long wavelength band with wavelength range 1565-1625 nm. It is the second lowest-loss wavelength band and is often used when C band is insufficient to meet bandwidth requirements. With the widespread availability of EDFA, DWDM systems have expanded up to L band and were initially used to expand the capacity of terrestrial DWDM optical networks. Now it has been brought in by undersea cable operators to do the same thing - expand the total capacity of undersea cables.
U Band
Because the transmission attenuation loss of C band and L band is the lowest, the signal light in DWDM system is usually selected to be at C band and L band. In addition to O band and L band, there are two other bands, namely the 850 nm band and the U band (ultra-long band: 1625-1675 nm). The 850 nm band is the main wavelength of multi-mode fiber communication system combined with VCSEL (Vertical cavity surface emitting Laser). U band is mainly used for network monitoring.
Summary
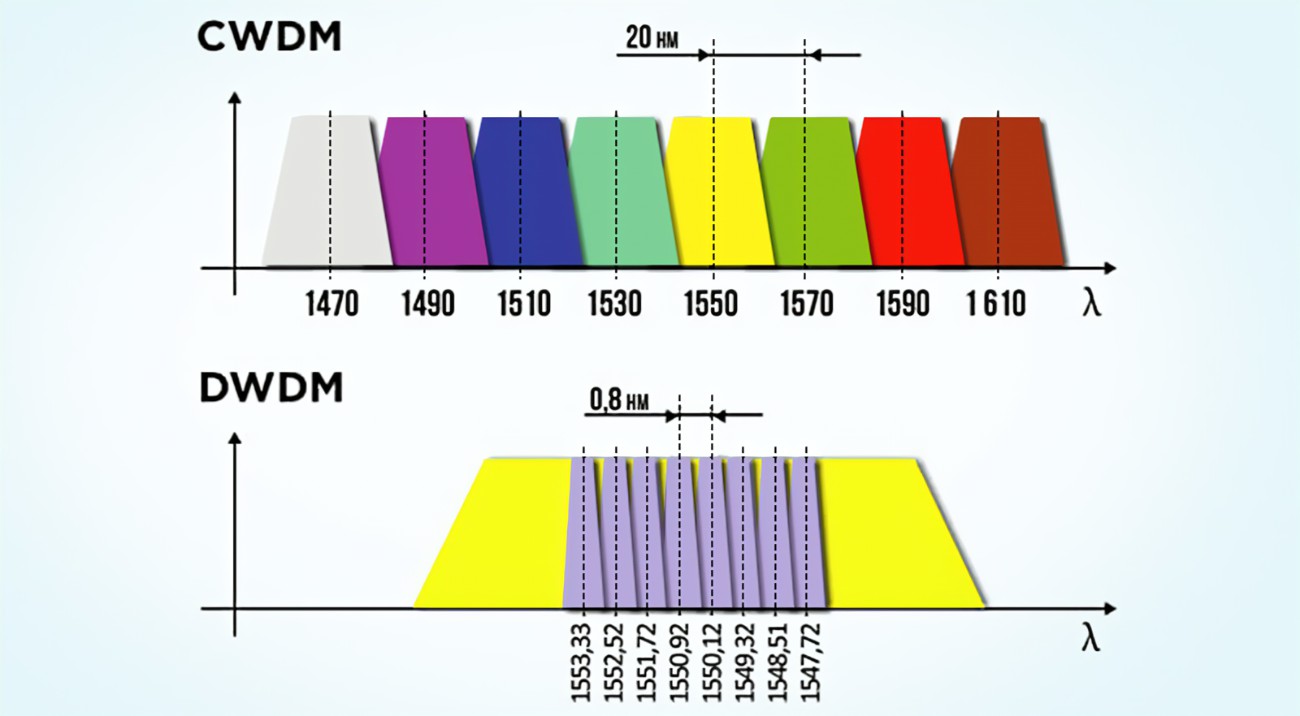
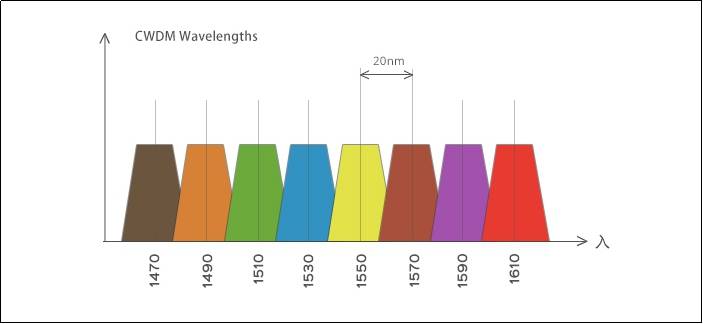
WDM technology can be divided into WDM, CWDM and DWDM according to different wavelength modes. The wavelength range stipulated by ITU for CWDM (ITU-T G.694.2) is 1271 to 1611 nm, but in application, considering the large attenuation of 1270-1470nm band, the band range of 1470~1610nm is usually used. DWDM channels are more densely spaced and use C-band (1530 nm-1565 nm) and L-band (1570nm-1610nm) transmission Windows. Ordinary WDM generally uses 1310 and 1550nm wavelengths. With the growth of FTTH applications, C band and L band, the most commonly used bands in fiber optic networks, will play an increasingly important role in optical transmission systems.





 Guanglong S&T Zone, No.8 High-tech Industry Park Chaoyang Road, Guilin ,Guangxi, China
Guanglong S&T Zone, No.8 High-tech Industry Park Chaoyang Road, Guilin ,Guangxi, China  +86-133-4600-8527
+86-133-4600-8527  alan.shizz@glsun.com
alan.shizz@glsun.com