Advantages and Applications of EDFA (Erbium-doped Fiber Amplifier)
What is EDFA
EDFA, short for Erbium-doped Fiber Amplifier, is one of the most commonly deployed amplifiers, featuring the capability of directly amplifying optical signals without the optical - electrical - optical signal converting process, which greatly boosts the capacity of fiber optic communication.
Advantages of EDFA
EDFA is a preferable option for long-haul DWDM systems, owing to its high pump power utilization, stable performance and mature technology.
1. High Gain
Gain value is one of the most important parameters of optical amplifier. The max gain of a qualified optical amplifier should reach 33dB, while that of an EDFA can reach 30~40dB. In addition, it provides good gain flatness over a wide wavelength band.
2. Low Noise
EDFA can spontaneously radiate noise, so it has low noise usually at 4~7dB. The crosstalk between each channel is minimal and multiple amplifiers can be cascaded. Its low noise feature makes it very suitable for long-haul application.
3. Low Loss
The working wavelength of EDFA is within the optimal waveband region (1500~1600nm) with minimum loss in fiber optic communication. The loss of coupling with optical fiber link is also minimum. Therefore, with low loss, EDFA can support longer transmission distance.
4. Wide Wavelength Band
EDFA frequency bandwidth is 20~40nm at 1550nm wavelength, and can realize multichannel transmission, thus increases transmission capacity.
5. Easy Deployment
Its simple structure makes it easier to couple with transmission fiber, making it more affordable compared with other signal amplification methods.
Applications of EDFA
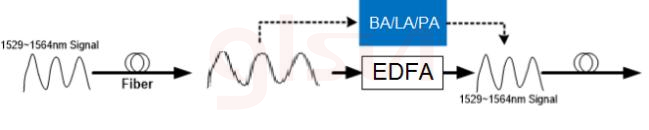
1. Power Amplifier
Deployed after optical multiplexer, it is used to enhance the power of multiple wavelength signal which is multiplexed, before processing transmission. Because the signal power after multiplexing is generally large, the requirement for noise index and gain of power amplifier is not very high, but relatively high output power is required after processing amplification.
2. Line Amplifier
Placed after power amplifier, it is used to periodically compensate the transmission loss of the fiber line. Generally low noise index and high output power are required.
3. Pre-Amplifier
Used before optical multiplexer and after line amplifer, it is used to amplify signal and improve receiver sensitivity. It requires low noise index, but not much for output power.








 Guanglong S&T Zone, No.8 High-tech Industry Park Chaoyang Road, Guilin ,Guangxi, China
Guanglong S&T Zone, No.8 High-tech Industry Park Chaoyang Road, Guilin ,Guangxi, China  +86-133-4600-8527
+86-133-4600-8527  alan.shizz@glsun.com
alan.shizz@glsun.com