Brief Introduction of Optical Transceiver Modules
The working principle of optical modules is to convert electrical signals into optical signals, or convert optical signals into electrical signals to realize photoelectric conversion and electro-optical conversion functions in optical fiber communication. Specifically, optical modules are mainly composed of optoelectronic devices (optical transmitters and optical receivers), functional circuits, and optical interfaces.
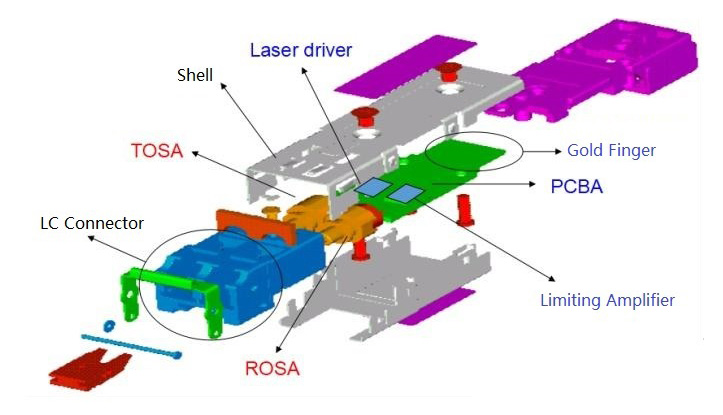
The Working Principal
At the transmitter end, the input electrical signal is processed by the driver chip, which drives a semiconductor laser (LD) or light-emitting diode (LED) to emit a modulated optical signal at a corresponding rate.
At the receiving end, the optical detection diode converts the received optical signal into an electrical signal, and outputs an electrical signal of the corresponding bit rate after passing through the preamplifier. The working principle of optical transceiver involves the process of photoelectric conversion and electro-optical conversion, and a variety of factors need to be considered, such as transmission rate, wavelength, transmission distance, etc.
Therefore, the performance index and characteristics of optical modules have an important impact on the transmission quality and transmission distance of optical fiber communication systems.
The schematic diagram of the optical module project is as follows:
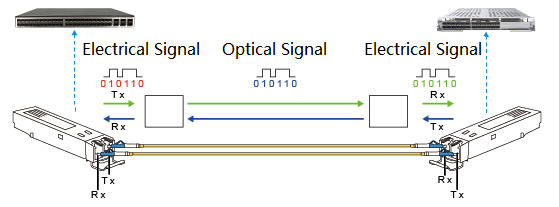
Type of Optical Transceiver Modules
There are many types of optical modules, and choosing the right optical module is crucial to the performance and stability of the optical fiber communication system
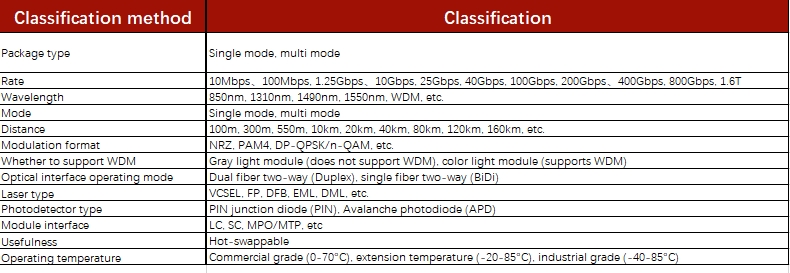
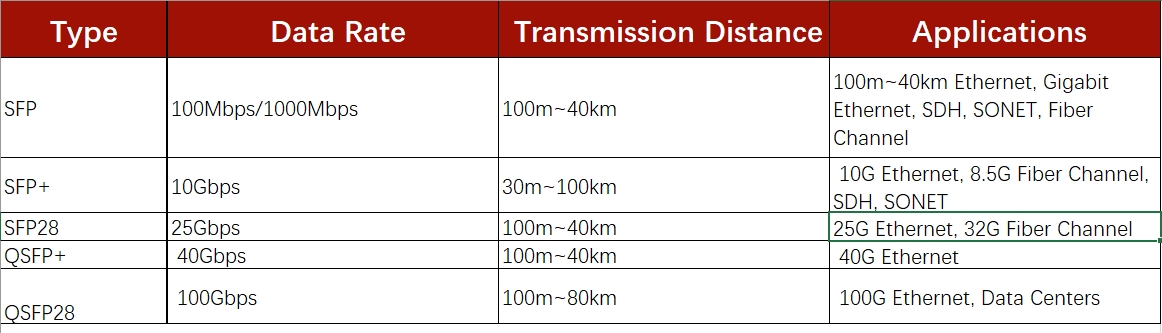
There are five types of optical module packages: SFP, SFP+, SFP28, QSFP+ and QSFP28, and the speed rates are 100M/1000M, 10G, 25G, 40G, 100G.
The naming of Optical Transceiver Modules
There are many types of optical modules, and different brands have their own unique optical module naming systems, but the industry has similar names for optical modules. The following explains the common naming conventions for optical modules:
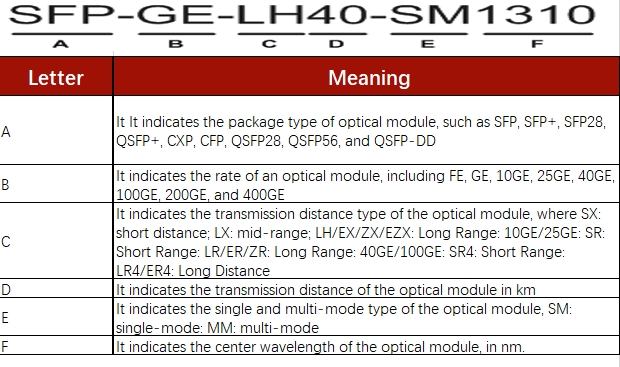
Key Parameters
There are many important photoelectric technical parameters for optical transceiver module, but for a hot plug optical module, the following three parameters are the most concerned when selecting:
1.Center Wavelength
850nm(MM, multi-mode, low cost but short transmission distance, generally only 500M);
1310nm (SM, single mode, large loss but small dispersion during transmission, generally used for transmission within 40KM);
1550nm (SM, single mode, small loss but large dispersion during transmission, generally used for long-distance transmission above 40KM, the farthest can be up to 120KM without any repeater)
In addition to the above conventional wavelengths, CWDM wavelength (SM, single-mode, color optical module) and DWDM wavelength (SM, single-mode, color optical module) are also used in multiplex transmission.
2.Data Rates
The number of bits of data transmitted per second (bit), in bps.
There are 7 types in common use currently: 155Mbps, 1.25Gbps, 2.5Gbps, 10Gbps, 25Gbps, 40Gbps, 100Gbps, etc. The transmission rate is generally downward compatible, so 155M optical modules are also called FE (100M) optical modules, 1.25G optical modules are also called GE (Gigabit) optical modules, and 10G optical modules are also called 10GE (10 Gigabit) optical modules. 10G optical modules are the most widely used module in optical transmission equipment currently. In addition, in the optical storage system (SAN), its transmission rate is 2Gbps, 4Gbps and 8Gbps.
3.Transmission Distance
The distance in kilometers (km) that optical signals can be transmitted directly without relay amplification. The transmission distance of the optical module is generally 550m for multi-mode, 20km, 40km, 80km and 120km for single-mode, etc.
Applications
Data Centers
There are lots of network switches, servers, etc in the main equipment room of the data center. They are the core of integrated wiring and information network equipment, and are also the data aggregation center of the information network system. The connection between servers, between switches, and between servers and switches requires the use of optical modules (direct-connected copper cables, active optical cables), fiber patch cables, and other transmission carriers to achieve data exchange.
Base Station
The base station of operator also needs optical transceiver modules to realize the interconnection between RRU and BBU devices. In the application, it needs to connect the links between these two devices, which requires optical transceiver modules and fiber patch cables. In 4G network, the devices used to connect the BBU and RRU are mainly 1.25G, 2.5G, 6G, 8G and 10G optical transceiver modules.
5G Bearer Network
The advent of the 5G era has indeed brought a new round of growth space to the optical module industry. The 5G bearer network is generally divided into metropolitan access layer, metropolitan convergence layer and metropolitan core layer to realize fronthaul and midhaul functions of 5G services. Among them, the interconnection between the devices of each layer mainly depends on the optical module.
Passive WDM System
Passive WDM systems are mainly used in metropolitan area networks, backbone networks, and wide area networks. CWDM optical transceiver modules and DWDM optical transceiver modules are commonly used. The CWDM optical module adopts CWDM technology, which can combine optical signals of different wavelengths through an external wavelength division multiplexer and transmit them through a single optical fiber, thereby saving optical fiber resources. At the same time, the receiving end needs to use a wave division multiplexer to decompose the complex optical signal.





 Guanglong S&T Zone, No.8 High-tech Industry Park Chaoyang Road, Guilin ,Guangxi, China
Guanglong S&T Zone, No.8 High-tech Industry Park Chaoyang Road, Guilin ,Guangxi, China  +86-133-4600-8527
+86-133-4600-8527  alan.shizz@glsun.com
alan.shizz@glsun.com